name: react_intro class: cols, middle, main .fifty.main-left[ # Interactive Front-end Development by Artem Halas and Stanislav Deviatykh ] .fifty.main-right[.main-circle[].secondary-circle[]] ??? Presenter display slide notes Pre-lecture checklist * Switching between mirroring and non-mirroring works * Unrelated tabs and windows closed or minimized * Do not disturb mode **ON** * Slides cloned, one has presenters mode on * Dependencies installed and scripts are working for lecture example code * Terminal(s) open with code and window to run scripts --- # Single Page Application (SPA) * A web application that requires a single page load in a web browser. * All changes to the DOM after the initial page load are done using JavaScript (via DOM APIs). * Examples: Gmail, Facebook, Google maps, Twitter, Instagram --- # JavaScript frameworks * 2007 Ember * 2009 Angular and NodeJS * 2010 Backbone - Use models, don't hold state in DOM * 2013 React - Declarative views, virtual DOM * so many more... --- # What differentiates JavaScript frameworks? Most framework designs are flavours of the [Model-View-Controller](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Model–view–controller) (MVC) pattern .cols[ .fifty[ * Model holds data and logic * View presents data * Controller passes data from model to views, accepts input from views and passes to model ] .full-image[] ] --- # What differentiates JavaScript frameworks? Differences usually come from * Template engine / support * Data-flow * State management * Means of composition --- # React * React solves View (with a bit of Controller) in Model - View - Controller. * Solves 1 problem and it solves it well - building reusable and testable components. * Library, not a framework. Doesn't make assumptions about your application, can use it in any existing application without problems! * Not all batteries are included! * Significant assembly might be required * Simple and declarative. --- # What is React * Works in native mobile applications through React Native. * Can be used to implement high-performance UIs * Scales when used in big teams. * [New beta documentation](https://beta.reactjs.org/) * [Old documentation](https://reactjs.org/) * Rethinking best practices by Pete Hunt: [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DgVS-zXgMTk](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DgVS-zXgMTk) * Excellent documentation * A lot of low-effort tutorials and blogosphere noise --- # React Developer Tools * [For chrome](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/react-developer-tools/fmkadmapgofadopljbjfkapdkoienihi?hl=en) * [For firefox](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/react-devtools/) * Open browser console and find out the state of each component --- # Templating Traditional web development suggested * All markup should be in templates * Templates can be reused for different data In practice * Templates introduce another (templating) language * It is usually not obvious what data a template needs * Refactoring templates can be difficult. It is not trivial to understand if, how and in how many places a template is used * Templating languages usually have limited capabilities * Often hard to test and debug --- # Templating Composing templates can be problematic * How to pass data to a nested template from a controller? * How does a controller receive input (e.g. from text fields) from a nested template? The solutions are usually rather complex --- # Control flow in templates * Reinvents JavaScript concepts (scope, context, control flow) * Sometimes through custom template-directives e.g. ng-repeat * HTML - HyperText Markup Language, not a programming language --- # React Problem: >> * Templates often do not work very well Solution: >> * Markup is defined using JavaScript. >> * Can be done with JSX or plain JavaScript. Drawback: >> * Does not work whatsoever when JavaScript disabled ??? Remember, we are only talking in the context of actual applications, so falling back when JavaScript is disabled is not too much of an issue here. --- # JSX ```js <button className='comment-form' onClick={props.onSubmit}> {props.text} </button> ``` --- # JSX * [https://reactjs.org/docs/introducing-jsx.html](https://reactjs.org/docs/introducing-jsx.html) * Optional in React (recommended in this course). * By far the most controversial part of React. * _Looks like_ HTML, but is a representation of HTML in JavaScript. * Transpiled to JavaScript (e.g. by a babel plugin) _Reminder_ >> Nothing works when user disables JavaScript. You are building an application, right? --- # JSX * Simplifies mapping JavaScript views to the HTML they generate. * Allows using JavaScript to generate all the markup. * No control flow through HTML extensions or another templating language! --- # React vs ReactDOM? * _React_ is a view library * _ReactDOM_ renders _React_ views in _DOM_ * Other renderers are possible * React Native renders React views using native (mobile) UI elements --- # Familiar Components ```html <div> <div> <label for="name">Text Input:</label> <input type="text" id="name" value="" /> </div> <div> <h4>Radio Button Choice</h4> <label for="radio-choice-2">Choice</label> <input type="radio" id="radio-choice-2" /> </div> </div> ``` .full-image[] --- # React Components * JavaScript function * Reusable UI element * Let you combines JS, CSS, markup ```js export default function Settings() { return ( <div> <a href="#">Link</a> </div> ); } ``` --- # Data flow Goals: * Getting data from JavaScript to HTML `Controller -> View` * Getting data from HTML (e.g. inputs) to JavaScript `View -> Controller` --- # Implicit two-way databinding .cols[ .fifty[ [Example](https://www.w3schools.com/angular/angular_databinding.asp) * When data in the model changes, the view reflects the change, * and when data in the view changes, the model is updated as well. ] .fifty[.full-image[]] ] --- # Implicit two-way databinding Easy and interactive in the beginning But, * an update to one view * can cause a model to update, * which can cause a different view to update, * which can cause another... --- # Implicit two-way databinding * can lead to performance issues * updates to controllers and views can happen with no apparent reason * data flow can be hard to understand --- # React - unidirectional data flow * React components have props * `props` are immutable * `props` are passed from parent component * If parent changes props of a child, child is fully re-rendered * Old child instance is thrown away (under-the-hood optimizations may occur) * Child does not need to worry about partial updates * A child component can never instruct its parent to change (one-way data flow) --- # Props example [Code example](https://github.com/urmastalimaa/interactive-frontend-development/tree/master/lecture_2/src/props_example) --- # State management State - the values of props (and internal state) of all components at one point in time. State management is the hardest thing to get right in an interactive application. --- # State management * Stateless components are very easy to reuse and understand * Components with complex state are very hard to reuse and understand * One unit of state should be managed in a single place * Managing overlapping state in various places across an application is a maintenance nightmare --- # React - isolate state mutations * Each React component can have state * State can only be changed by the very component that defines it * No surprise updates to state! * If state is an object, new state is merged into the old one --- # React - isolate state mutations * Component and its children re-render **whenever state or props change** * Child components can only use callback functions to notify parents about updates * No implicit `View -> Controller` data-binding * The callback function in a parent can in turn invoke a callback that it got from its parent all the way to the root component --- # Before React ```html <!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <body> <button id="btn">Click me</button> </body> <script type="text/javascript" src="./app.js" defer=true></script> </html> ``` ```js const button = document.getElementById('btn') button.addEventListener('click', setClicked) function setClicked() { button.innerText = `Clicked`; } ``` --- # React classes ```jsx import { Component } from 'react'; class OneClickButton extends Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { clicked = false }; this.setClicked = this.setClicked.bind(this); } setClicked(event) { this.setState({ clicked: true }); } render() { const text = this.state.clicked ? "Click me" : "Clicked"; return <button onClick={this.setClicked}> {text} </button>; } } ``` --- # More on prototypical inheritance [https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Inheritance_and_the_prototype_chain](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Inheritance_and_the_prototype_chain) --- # React hooks * Special functions starting with ”use” that let you “hook into” React state and lifecycle features * Can only be called at the top level of your components or custom hook * Don't call Hooks inside loops, conditions, or other nested functions * Think of them as declarations about your component’s needs * You will meet the other hooks later --- # React hooks * Functional components using hooks: * Greatly improve readability as the hooks repeat standard patterns * Sacrifice readability for the uninitiated by being _magic_ * Allow injecting application logic to the UI without needing class-based components --- # React hooks - useState ```jsx import { useState } from 'react'; export default function OneClickButton() { const [clicked, setClicked] = useState(false); const setButtonToClicked = () => setClicked(true); const text = clicked ? "Click me" : "Clicked"; return ( <button onClick={setButtonToClicked}> {text} </button> ); } ``` ??? Data flows up You'll almost never want to keep a sentence, such as "Click me" in state as that is purely a rendering concern. --- # React hooks - useState How does React know which state to return? ```js let hooks = []; let index = 0; const useState = (initialValue) => { let pair = hooks[index]; if (pair) { index++; return pair; } const setState = (nextState) => { pair[0] = nextState; updateDOM(); } pair = [initialState, setState]; hooks[index] = pair; index++; return pair; }; ``` --- # Where to hold state? * Identify components that depend on shared state * Identify a common parent of those components * Either the common parent or a component higher up should own the state * Components should only have state that they are fully responsible for * A component dealing with very particular state is not reusable * General application state should be pushed "up", to a root component --- # Keeping most state in root component * All child components are re-rendered when state changes * Simple, modular and fast. --- .full-image[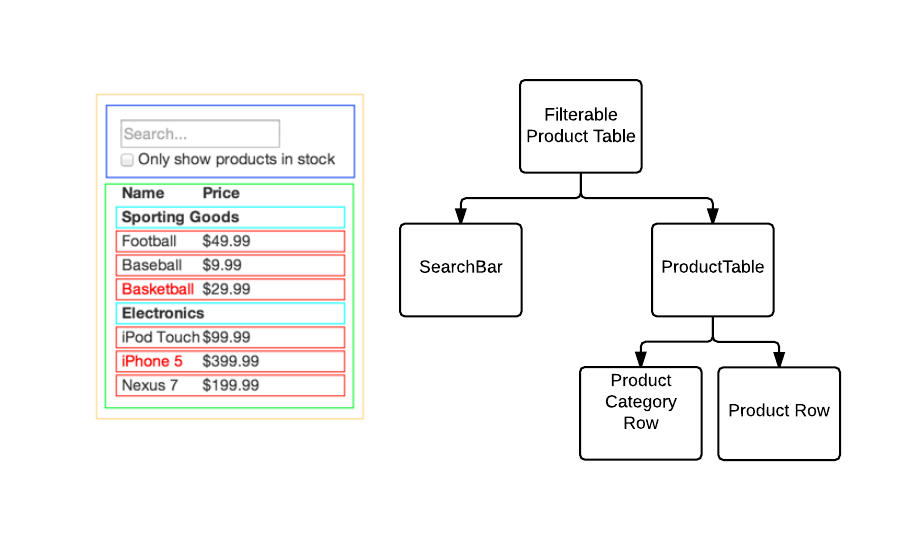] .footer[From: https://blog.risingstack.com/the-react-js-way-flux-architecture-with-immutable-js/] ??? Picture from: https://blog.risingstack.com/the-react-js-way-flux-architecture-with-immutable-js/ --- # State example [Code example](https://github.com/urmastalimaa/interactive-frontend-development/blob/master/lecture_2/src/state_example) --- # What about performance? Isn’t re-rendering everything whenever a smallest thing changes slow? --- # Virtual DOM * Changing the DOM has historically been very slow * DOM API is not declarative, relies on mutations, optimizations are difficult * ```js element.innerHTML = "..."; ``` * Re-rendering DOM elements causes flickering and loses DOM state (e.g. _focus_). * _Virtual DOM_ - a virtual representation of the real DOM in JavaScript --- # Virtual DOM On every update * Build new Virtual DOM subtree * Diff it against the old subtree * Compute the minimal set of real DOM mutations and put them into a queue * Batch execute all the real DOM mutations * https://reactkungfu.com/2015/10/the-difference-between-virtual-dom-and-dom/ --- # Virtual DOM * All DOM operations done on **virtual** DOM * **Real** DOM changed in batches * Automatic event (e.g. _click_) delegation * Seamless user experience when re-rendering all the time ??? Virtual DOM is not unique to React. It's now used in a variety of libraries and also on its own. This signals that Virtual DOM is a good idea regardless of React. --- .full-image[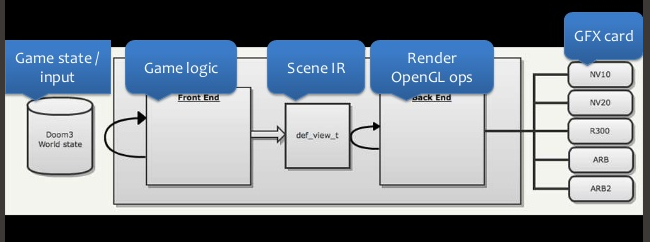] .full-image[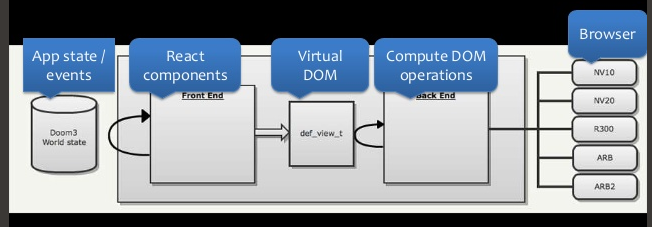] .footer[[https://lincolnloop.com/blog/architecting-your-app-react- part-1/](https://lincolnloop.com/blog/architecting-your-app-react- part-1/)] ??? Similarities between vDOM and Doom3 rendering cycles. --- # Well-defined React Components * A good React Component is a _pure function_ of its props > A _pure function_ is a function where the return value is only determined > by its input values, without observable side effects * _Composition_ of such pure React Components is also _pure function of its props_ * Implement React components as pure functions of props, no classes required * [Official documentation](https://reactjs.org/docs/components-and-props.html#functional-and-class-components) --- # Pure function component example [Code example](https://github.com/urmastalimaa/interactive-frontend-development/blob/master/lecture_2/src/pure_function_example) --- # Prop validation * React provides tools to validate type and presence of component props. * This run-time validation is only performed in development environment. * Errors/warnings can be seen in tests(!) or browser console. * [Official documentation](https://reactjs.org/docs/typechecking-with-proptypes.html) --- # Props validation example [Code example](https://github.com/urmastalimaa/interactive-frontend-development/tree/master/lecture_2/src/pure_function_example#prop-validation) --- # Form fields * React component and its state must reflect the DOM and its state * How to link React components with inputs? --- # Form fields * ```js const field = <input type="text">; ``` Define _text_ input field * ```js const field = <input value={someValue}>; ``` Set value of the input field. If value is a constant, input **cannot be changed** by user. --- # Form fields * ```js const field = <input onChange={someFunction}>; ``` Callback function invoked whenever input changed by user * ```js const field = <input onKeyUp={someFunction}>; ``` Callback invoked when any button is released (can check for `keyCode`) --- # User input example [Code example](https://github.com/urmastalimaa/interactive-frontend-development/blob/master/lecture_2/src/user_input_example/README.md) --- # Constructing pure functions * Two basic JavaScript constructs: * **Objects** (key -> value) * **Arrays** * ES5 is lacking ways to easily construct new objects without mutating * Always use pure functions to create new props or state, **never mutate** _props_ or _state_ * Avoid mutation whenever you can [Creating new arrays/objects without mutations](https://github.com/urmastalimaa/interactive-frontend-development/blob/master/lecture_1/src/PureFunctions.js) --- # React official guides Excellent tutorials, examples and API documentation * [Getting started](https://reactjs.org/docs/getting-started.html) * [Hello word](https://reactjs.org/docs/hello-world.html) * [Adding React to a website](https://reactjs.org/docs/add-react-to-an-existing-app.html) --- # Homework [Requirements](https://github.com/urmastalimaa/interactive-frontend-development/blob/master/homework/weather/exercise2.md) **Only submit what is yours** Deadline 06/03/2022 23:59 Unit tests for **React components only** are **not** mandatory --- # Homework If you need to provide further information, include it in README.md. Submit zipped file to https://courses.cs.ut.ee/2022/react/Main/Submit Don’t include node_modules/ or .git/, .hg/, .svn/, make sure that your zipped file size is reasonable. You can use/modify/extend [this script](https://gist.github.com/urmastalimaa/70edc0728cb711234f42) (usage: `node zipHomework.js`) to automate zipping. --- class: middle, center <video width="100%" height="50%" controls> <source src="assets/lecture-2/hm2.mov" type="video/mp4"> Your browser does not support the video tag. </video>